No More Mistakes with Flour Mill Machine Manufacturer
Mar 11 2023
In today’s digital-first world, cloud computing has become a cornerstone for businesses of all sizes. From startups to large enterprises, organizations are rapidly adopting cloud services to improve agility, scalability, and innovation. However, with great power comes great responsibility - especially when it comes to managing costs.
Cloud FinOps, short for Cloud Financial Operations, is a practice that combines financial management, operational best practices, and cloud technology to optimize and control cloud spending. It enables organizations to gain visibility, accountability, and efficiency in their cloud usage by aligning teams around cost management, usage tracking, and budgeting, ultimately helping businesses maximize the value of their cloud investments.
Cloud FinOps, short for Cloud Financial Operations, is the practice of managing and optimizing cloud spending through collaboration between finance, technology, and business teams. It’s a cultural and operational framework designed to bring financial accountability to cloud usage while empowering technical teams to innovate quickly and cost-effectively.
Unlike traditional IT infrastructure, cloud computing typically operates on a pay-as-you-go model. While this flexibility offers many benefits, it can also lead to unexpected spikes in costs if not properly managed. Organizations often struggle with “cloud bill shock” — when the monthly cloud invoice is far higher than anticipated.
Cloud providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer a vast array of services and pricing models, making it challenging to understand and predict costs. Without a clear grasp of consumption patterns and pricing structures, organizations risk overspending or underutilizing resources.
Cloud spending touches multiple parts of the business—developers deploy resources, finance teams handle budgets, and business leaders set priorities. Cloud FinOps fosters collaboration across these groups to align cloud usage with business goals.
Real-time insights into cloud usage and expenses enable businesses to make data-driven choices more quickly. This agility supports innovation while maintaining financial discipline.
Cloud FinOps is guided by a few fundamental principles that help organizations adopt and sustain best practices:
Collaboration and communication between engineering, finance, and leadership are essential for efficient cloud cost management. By breaking down silos, teams can understand their impact on cloud spending and work together to optimize it.
Rather than assigning cost management to a single department, Cloud FinOps encourages every stakeholder to take responsibility for their cloud consumption and its financial implications.
Cloud FinOps is not a one-time effort. It involves ongoing monitoring, reporting, and adjusting strategies as cloud usage evolves.
It is essential to have up-to-date, precise statistics about cloud utilization and expenses. This transparency enables teams to identify waste, forecast budgets, and justify cloud investments.
To implement Cloud FinOps successfully, organizations typically focus on several key areas:
Visibility is the foundation of Cloud FinOps. Organizations must have access to granular cloud usage and cost data - broken down by teams, projects, or applications. This often involves integrating cloud provider billing data into centralized dashboards or financial management tools.
Cost allocation assigns cloud expenses to the responsible teams or projects. Chargeback or showback mechanisms help teams see their cloud consumption in financial terms, promoting accountability and more thoughtful resource usage.
Budgets and predictions can be made more accurately by organisations using consumption trends and historical data. Cloud FinOps teams track variances and adjust forecasts as needed to prevent budget overruns.
Optimization focuses on identifying idle resources, overprovisioned services, or inefficient configurations. This could include rightsizing instances, using reserved or spot instances, and automating shutdowns of unused resources.
Governance policies help set guardrails for cloud spending, such as spending limits, approval workflows, and tagging standards. These controls ensure compliance and reduce the risk of uncontrolled expenditure.
Organizations that embrace Cloud FinOps can unlock several key benefits:
Businesses may drastically cut their cloud spending without sacrificing performance by detecting waste and optimising resource usage.
Accurate insights from Cloud FinOps enhance financial reporting, forecasting, and budgeting.
Bringing together finance and technical teams leads to shared accountability and a culture of cost-conscious innovation.
With real-time cost visibility, teams can experiment and iterate rapidly, knowing the financial impact of their decisions.
Cloud FinOps makes cloud costs visible to all stakeholders, reducing surprises and building trust across the organization.
Cloud FinOps has many benefits, but there are drawbacks as well:
Complexity of Cloud Pricing Models: Navigating the intricate pricing structures of various cloud services can be overwhelming.
Cultural Change: Shifting organizational mindset to shared ownership of costs requires training and communication.
Tooling and Integration: Implementing Cloud FinOps tools and integrating data sources can be technically demanding.
Keeping Pace with Cloud Innovation: Cloud providers frequently update offerings and pricing, requiring constant learning and adjustment.
Many tools exist to assist with Cloud FinOps practices, including:
Cloud provider native tools: Google Cloud Billing, AWS Cost Explorer, and Azure Cost Management.
Third-party FinOps platforms: Cloudability, Apptio, CloudHealth, Spot.io.
Financial management tools: Integration with ERP or accounting software to align cloud costs with broader business financials.
The size, complexity, and infrastructure of your company all influence the tools you use.
If you’re ready to start your Cloud FinOps journey, here are a few practical steps:
Build a cross-functional team: Bring together finance, engineering, and business stakeholders.
Establish cloud cost visibility: Set up reporting tools and dashboards for detailed insights.
Define governance policies: Create rules and guidelines for cloud usage and spending.
Educate and communicate: Train teams on cost management best practices and cloud pricing.
Implement cost optimization processes: Regularly review usage, identify waste, and adjust resources.
Iterate and improve: Continuously refine your Cloud FinOps strategy based on feedback and data.
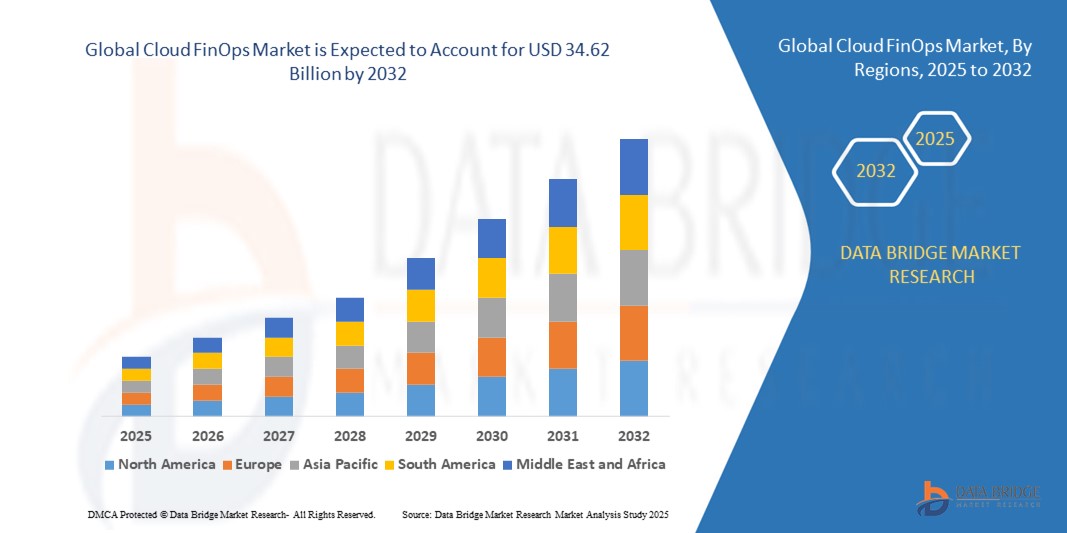
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global cloud finops market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.10% from its 2024 valuation of USD 11.24 billion to USD 34.62 billion by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cloud-finops-market
As cloud computing continues to grow, managing its financial implications becomes more critical. Cloud FinOps offers a structured approach to balancing innovation and cost control by fostering collaboration, transparency, and data-driven decision-making.
Social Media Marketing Strategies for Beginners
Mar 14 2023
(0) Comments