No More Mistakes with Flour Mill Machine Manufacturer
Mar 11 2023
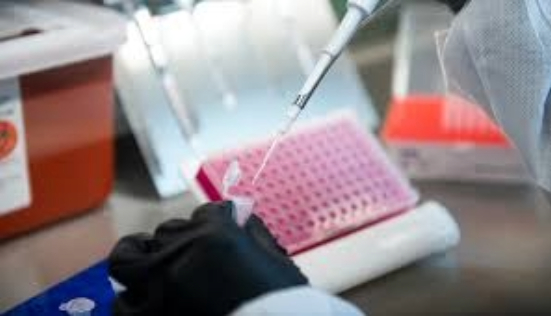
An assay is an investigative analytical technique that helps to identify and quantify an analyte, perform its structural characterization, and determine its function. It finds application in diverse fields, such as the pharmaceutical and medical research industry, environmental and molecular biology, and mining. Assay testing is performed in bioanalytical laboratories using commercially available assay kits or newly developed assays under controlled conditions.
It is well-known that a drug may require approximately 12 to 15 years and a million dollars to reach the market. Within this timeframe, it takes about 3 to 6 years to determine the drug efficacy in an animal model after extensive testing in the drug discovery phase. Despite extensive testing, one-third of drugs fail at the first stage of clinical trials. Half of them show toxicity in humans, while the other half fail to display desired efficacy in humans during clinical trials. Thus, it is prudent to test the effectiveness and safety of drugs using in vitro and cell-based assays in the early stages of drug development.
Assays are indispensable tools in drug discovery and development. They help to screen drug targets and compound libraries to identify potential hits and optimize lead compounds. They are also used to measure the biological activity of potential drug candidates and determine their efficacy and safety.
There are different types of assay formats, each with a set of advantages and limitations. The choice of the assay depends on the specific goals of the study. Assays can be broadly categorized as ligand-binding assays (measuring the binding between a ligand and a receptor), bioassay (measuring biological activity in response to stimuli), and immunoassay (detecting the binding of antigens and antibodies).
Alternatively, we can characterize assays as biochemical and cell-based. Biochemical assays can examine the target receptor and identify compounds that display desired activity towards the receptor. Cell-based assays, on the other hand, can measure the biological effect of a drug on living cells. In addition to biochemical and cell-based assays, animal model assays are also commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry. Animal model assays assess the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a drug, along with drug toxicity and its maximum tolerated dosage.
Without assays, drug discovery and development would become extremely difficult and time-consuming. Thus, it is pivotal to develop top-notch assays to facilitate each step.
Must Read: What is the Working Principle of LC-MS Mass Spectrometry?
Quality control is a routine and compulsory task in clinical and bioanalytical laboratories. Quality control practice broadly encompasses analysis of reference/standard materials (quality controls), including appropriate blanks and controls (positive and negative) in the protocol, and comparing experimental values to the expected distribution under stable laboratory conditions.
Results from assays need to be precise, accurate, reliable, and valid. Quality control is pivotal in fulfilling these requirements in assay development, validation, and testing. First, a calibration protocol needs to be established and should be performed at the beginning of testing. These can be done using appropriate quality control materials. Quality controls are primary indices that help determine an assay’s performance and are crucial elements in an assay’s lifecycle management. In addition to reference standards, in-house developed standards may be used. Second, adding an internal control (positive and/or negative) in each plate can help monitor the quality of assay results. Third, documenting all processes, procedures, and deviations. Fourth, it is vital to ensure that the laboratory conditions are stable per assay requirements. Fifth, it is essential to validate laboratory processes and perform variability and proficiency testing. This step involves correlating inter-plate and intra-plate assay results for specimens. This approach gives a sense of accuracy and reliability of the assay results. Estimating the coefficient of variation and correlation coefficient of assay results can help monitor the quality of the assays. Finally, a protocol should be established for handling discordant results appropriately.
In addition to the steps mentioned above that comprise some of the best practices of quality control in Assay Testing, several other actions can help to strengthen quality management in bioanalytical laboratories. These include adequate and trained staff capable of conducting standard and specialized assay procedures effectively and safely. Standard operating procedures provide detailed step-by-step instructions for a process. Thus, implementing standard operating procedures can be helpful. Regular maintenance checks on equipment are of paramount importance in quality control as they can not only reduce errors but also avoid costly downtime. Introducing a quality management system in the laboratory can help keep a record of various laboratory procedures and help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Inventory management software can help track the reagents, and an efficient data management system can help manage the data generated from the assays and other tests.
Assay testing is a crucial and routine bioanalytical procedure in the pharma and biotech industry, particularly in drug discovery and development. Accuracy and precision, specificity, reproducibility, relevance, interference, and affordability are some of the desired criteria of an assay. Adhering to best practices for quality control in a Bioanalytical Laboratory can help ensure that these criteria of an assay are fulfilled and the procedures comply with the regulatory requirements.
Social Media Marketing Strategies for Beginners
Mar 14 2023
(0) Comments